Introduction: Choosing the Best Server Drives – HDD vs SSD
The efficiency and performance for your server can make or break your business or data center. It is crucial to select the right server storage solution if you are running an e-commerce website with high traffic, managing enterprise databases, or hosting virtual machines. One of the most common arguments about server hardware is whether to use Server HDDs or Server SSDs for your servers. To understand the server storage comparison between these two technologies is key to selecting the best drive for servers.
This in-depth guide compares the differences between Server HDDs and SSDs, their primary pros and cons, performance benchmarks and which option is best suited for your server setup. It will help you make an informed choice about your server hard drives.
Understanding Server Storage Basics: Server HDD and Server SSD
It is essential to understand the fundamental technologies behind server HDD and server SSD to select the best drive for servers. Both are used for server data storage, but employ vastly different mechanisms.
What is a Server HDD?
A hard disk drive (HDD) is a traditional storage device that uses spinning magnetic platters to read and write data. Server HDD units are designed for 24/7 operation, making them more reliable and long-lasting than consumer-grade models. They usually have large capacities, ranging from 1TB to 18TB or more, which makes them ideal for storing a large amount of data at a low cost per GB. They are a good choice for HDD for server applications where raw capacity and cost are the primary considerations.
Key Features of Server HDDs:
- Mechanical parts and magnetic storage are two essential features of server hard drives.
- High-capacity storage for server data that doesn’t cost a lot
- Sequential read/write speeds are usually between 100MB/s and 250MB/s.
- SATA and SAS are standard interfaces.
- Noticeable noise level of hard drives due to mechanical operation
What is a Server SSD?
Solid-state drives (SSDs) are much faster and more durable than hard disk drives (HDDs) because they use NAND flash memory to store data. Because SSDs for servers don’t have any moving parts, they can access data faster, use less power, and run more quietly. Server SSDs are designed to handle high-speed performance, large-scale virtualization, and essential workloads. It makes them a strong candidate for the best server drive in demanding environments. This category also includes specific factors comparing Enterprise SSDs vs consumer SSDs, with enterprise versions offering better write endurance and reliability.
Key Features of Server SSDs:
- Flash memory-based, with no moving parts, which contribute to the high durability of SSD.
- Boot and access times are faster, which makes performance comparisons better.
- Read/write speeds can be as low as 500MB/s (SATA) or as high as 7000MB/s (NVMe), which gives better IOPS performance.
- Common interfaces are SATA, SAS, and NVMe (PCIe).
- Quiet operation, which lowers the noise level of hard drives in data centers.
Core Comparison: Server HDD vs Server SSD in Server Environments
This table provides a quick performance comparison and highlights the main differences when considering HDD vs SSD for your server.
HDD vs SSD – Key Differences at a Glance: A Server Storage Comparison
To make the right investment, you need to understand the key differences between server storage comparison. This section provides more detailed information about the key metrics for Server SSD and Server HDD.
1. Performance Comparison: Read/Write Speed and IOPS Performance
When it comes to read/write speed and IOPS performance (Input/Output Operations Per Second), SSDs are much better than HDDs. NVMe SSDs, in particular, have very low latency and high throughput which making them ideal for databases, virtualization, AI applications, and fast-paced data center storage. This makes SSD for server the superior choice where speed is paramount.
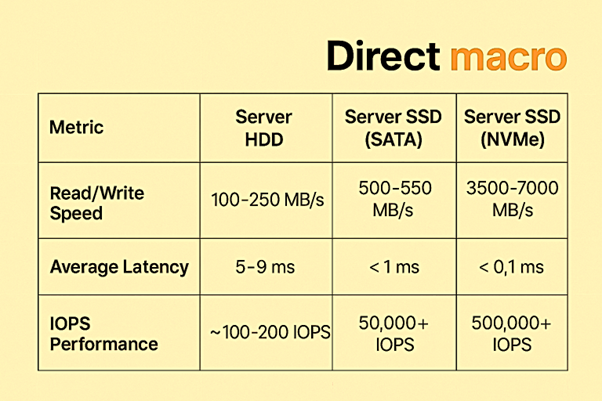
Result: SSDs outperform HDDs in environments where performance is crucial. Server SSD is the best drive for servers that need high IOPS performance and low latency.
2. Cost per GB: Evaluating Server Storage Investment
One of the best reasons to use Server HDDs is that they are cheap. Even in 2025, HDDs for servers still maintain less cost per GB than SSDs, particularly for larger models such as 8TB, 12TB, or 18TB. This makes Server HDD a compelling option for server data storage where capacity outweighs immediate speed needs.
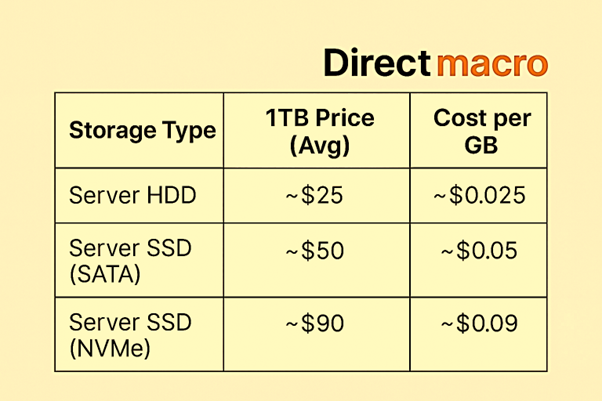
Result: HDDs for server remain the best choice for budget-conscious users seeking high-capacity server storage comparison. HDDs might be the better choice if your server setup values capacity over speed (for example, backup servers or archive storage). SSDs for servers are worth the extra cost per GB if speed and responsiveness are your top priorities (for example, apps that customers use or live environments).
3. Durability of SSD & Lifespan of Hard Drives
When evaluating server hard drives, the length of their lifespan and their durability are crucial considerations. HDDs are more susceptible to damage because they have numerous moving parts. SSDs are more durable than HDDs because they don’t have any mechanical components. They are also less likely to lose data when they are vibrated or shocked, which makes them better for demanding data center storage. However, write endurance is an essential factor for SSDs for servers, because flash memory cells wear out after a certain number of write cycles. This is especially important when comparing enterprise SSDs to consumer SSDs, as enterprise drives are designed for much higher write endurance.
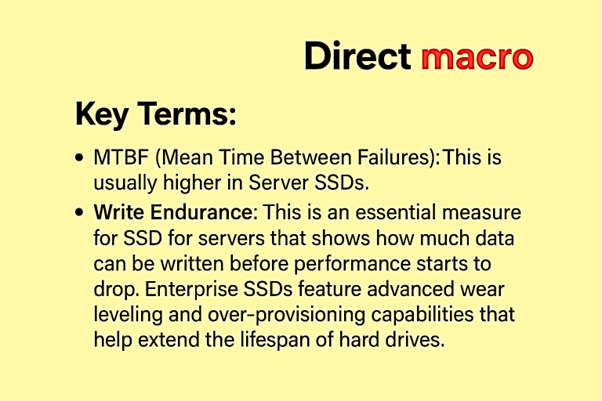
Result: SSDs are usually more durable and reliable in challenging situations, because they are made of solid-state materials. The durability of SSD gives you a lot of peace of mind when it comes to server data storage.
4. Power Efficiency: Optimizing Data Center Storage
SSDs use significantly less power than HDDs because they don’t have spinning disks or moving heads. This means that data center storage environments will generate less heat and have lower cooling costs, which contributing to better power efficiency. This is a big advantage for large-scale server deployments.
Result: SSDs use less energy and are more environmentally friendly, which means that server storage will be less costly to run in the long run.
5. Form Factors and Interfaces: SATA vs NVMe for Server Hard Drives
There are many common form factors and interface options for both types of server storage. This affects how well they work with different server hard drives.
Form Factors
- Server HDDs: Usually 3.5″ (common for servers) and 2.5″.
- Server SSDs:5″ (SATA), U.2 (SAS), M.2 (NVMe), and add-in cards (PCIe).
Common Interfaces
- Server HDD: SATA III, SAS 12Gbps
- Server SSD: SATA III, SAS, NVMe (PCIe 3.0/4.0/5.0)
Understanding the differences, especially between SATA and NVMe, is crucial for maximizing the performance of your server data storage.
Server Storage Use Cases: Selecting the Right Server Hard Drives
The choice between Server HDD vs SSD hinges on your specific use cases for SSD and HDD. Each drive excels in different server environments. This table illustrates typical use cases for SSD and HDD for optimal server storage comparison.
Best Use Cases – HDD vs SSD for Servers: Database vs Archive Storage
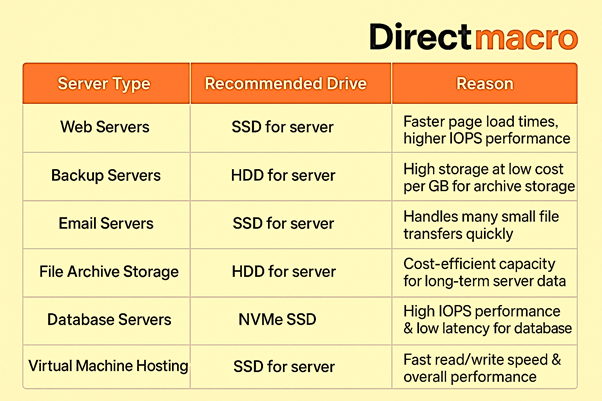
Server HDD vs SSD: Real-World Scenarios for Optimal Server Data Storage
Let’s examine some real-world examples that illustrate the best choice between Server HDD vs SSD for various server storage comparison needs.
Example 1: Web Hosting Company – Prioritizing SSD for Server Performance
Uptime and page load speed are very important for a company that hosts hundreds of websites. SSDs for servers enable faster file access, quicker database query execution, and quicker response times to requests. In this case, an NVMe SSD array improves both performance comparison and user experience, demonstrating why SSD for server are the best drives for web hosting.
Example 2: Archival Storage Provider – The Role of HDD for Server Data
For a company that provides long-term backups and cold storage, having enough space is critical, but having quick access is not. Enterprise HDDs for servers are the best option because they provide the most cost-effective server data storage for archive storage. The Server HDD is the best option due to its lower cost per GB.
Example 3: Financial Firm with Real-Time Trading Data – Best Drive for Servers
A bank that handles millions of transactions daily requires the ultra low latency and the highest level of dependability. A RAID-configured NVMe SSD setup is best for this situation because it has high IOPS performance and fast read/write speeds. This clearly illustrates when an SSD for server becomes the best drive for servers in critical, performance-driven environments.
Technical Features: Understanding Server SSD Technologies
There are more than just fundamental differences between HDDs and SSDs. Some technologies can extend the lifespan of hard drives and improve their performance, which is particularly important for enterprise SSDs vs consumer SSDs.
1. TRIM
TRIM lets the operating system to inform an SSD which blocks of data are no longer in use and can be erased from the inside. This proactive management maintains a steady read/write speed, enhancing the SSD’s performance over time.
2. Wear Leveling
Wear leveling ensures that write operations are spread evenly across the SSD’s memory cells. It stops some cells from wearing out too quickly. It is crucial for extending the durability of SSD and overall lifespan of hard drives in server SSD deployments.
3. Garbage Collection
Garbage collection helps keep memory blocks organized and clean, which maintains consistent SSD performance and reliability, ultimately extending the lifespan of the SSD for server.
SATA vs NVMe: Which Interface is Better for Server SSDs?
The interface primarily determines how quickly an SSD for server can read and write data, as well as its overall performance. To optimize your server data storage, it is essential to understand the differences between SATA vs NVMe.
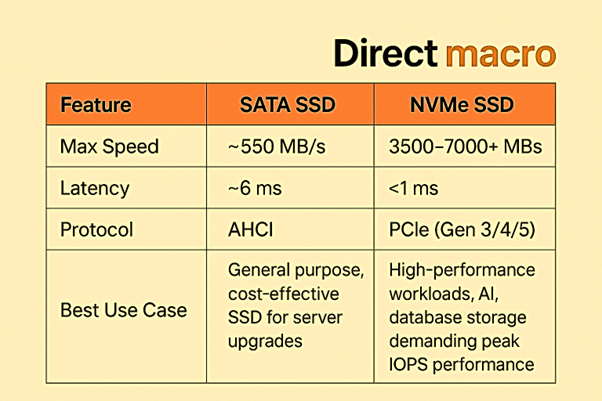
Result: Use SATA SSDs for upgrades that don’t require a significant investment, as well as for general-purpose server storage. Choose NVMe SSDs. if you need the fastest drives for servers in terms of performance comparison and read/write speed,
Hybrid Storage Strategy: The Best of Both Worlds for Server Storage
Many businesses use a mix of SSDs and HDDs for server storage. They use SSDs for frequently accessed “hot” data and HDDs for larger amounts of “cold” data. This smart way to compare server storage helps find a good balance between cost per GB and performance.
- Server SSDs: Best for operating systems, active databases, and “hot” data that needs fast read/write speeds and high IOPS performance.
- Server HDDs: These are great for log files, archives, backups and big datasets where cost per GB and capacity are more important than immediate access speed like archive storage.
Pro Tip: Utilize a tiered storage architecture or caching solutions to manage and optimize resource allocation dynamically. It ensures that the best drive for servers is always used for the right task. It improves the overall efficiency of server data storage.
Future Trends in Server Storage 2025 and Beyond
The world of server storage is constantly changing. Several new technologies will change the HDD vs. SSD debate in the years to come:
- PCIe Gen 5.0 NVMe SSDs are becoming more common. They have even higher throughput (up to 14 GB/s), which pushes the limits of SSD performance.
- QLC NAND SSDs are getting better, offering more space at a lower cost per GB for SSD server solutions.
- AI-powered storage tiering will automatically move data placement across different server hard drives (SSDs and HDDs) based on real time access patterns. It will improve power efficiency and performance comparison.
- New technologies like Heat-Assisted Magnetic Recording (HAMR) are pushing HDD capacities over 20TB, making them still useful for significant archive storage needs and challenging the lifespan of hard drives benchmarks
Final Verdict: Optimal Server Storage – SSD or HDD for Your Server?
Ultimately, the decision between SSD or HDD for your server depends on your operational requirements and budget.
- Put server SSDs, especially NVMe SSDs, at the top of your list for the best speed, performance comparison, and low latency. They are the best drives for servers that require handling heavy, real-time workloads.
- Enterprise HDDs are still delivering exceptional value as reliable server hard drives for archiving, backups, and bulk storage where cost per GB is the most important thing.
If possible, invest in a hybrid server storage solution to maximize efficiency and ROI by leveraging the strengths of both SSD for server and HDD for server.
Shop the Best Server Storage Drives at Direct Macro
We offer a wide selection of enterprise-grade HDDs and SSDs from reputable brands, including Seagate, Western Digital, Samsung, and Intel, at Direct Macro. We have the correct server storage solution for your business, whether you need super-fast NVMe drives for peak IOPS performance or reliable high-capacity HDDs for server archive storage.
Check out our full range of server storage options and upgrade your infrastructure today! Find the best server drive to fit your needs.
For more assistance, contact us at (855) 483-7810 or visit our website for bulk orders.
Final Thoughts
As prices decline and enterprise-grade NVMe SSDs become more prevalent, many businesses are transitioning away from traditional HDDs, particularly for server tasks that demand high performance. SSD for servers offers several advantages, including faster read/write speeds, improved IOPS performance, and reduced power consumption.
HDDs for servers, on the other hand, remain a practical option. They are still the best value for money when it comes to cold storage, archiving, and backups. This makes the server storage comparison hard but a hybrid approach makes it easier.
Direct Macro has both high-performance server SSDs and reliable enterprise HDDs to meet all of your business needs. Explore our selection and enhance your server infrastructure today. Ensure you select the most suitable and best drive for servers for every application.
FAQs
Is SSD better than HDD for servers in 2025?
Yes, SSDs have significantly faster read/write speeds, higher IOPS performance, and improved power efficiency. They are ideal for tasks that require high performance, such as databases, virtualization and web hosting. But HDDs are still an excellent choice for bulk storage and backups because they cost less per GB.
Which is more cost-effective: SSD or HDD for server storage?
HDDs are cheaper per GB, making them better suited for server storage that requires cost-effective solutions, such as backups and archive storage. SSDs cost more, but they are faster and more reliable, especially on live servers, which makes them a better choice for performance.
What is the difference between enterprise SSDs and consumer SSDs?
Enterprise SSDs are designed for24/7 server workloads that require higher write endurance, MTBF, and features such as power-loss protection. On the other hand, consumer SSDs are made for lighter and everyday tasks. The difference between enterprise SSD vs consumer SSD is significant for the long-term server data storage.
Can I use both HDD and SSD in the same server?
Yes. Many servers employ a hybrid storage setup, utilizing SSDs for fast server applications and HDDs for large-scale storage needs. It strikes a balance between performance and cost-effectiveness for storing large amounts of data on servers.
Is NVMe better than SATA SSD for servers?
Compared to SATA SSDs (~550 MB/s), NVMe SSDs are significantly faster (up to 7,000+ MB/s) and have lower latency. They offer the best IOPS performance for servers that handle a high volume of work involving AI, virtualization and real-time analytics.
